If you’ve lost teeth and haven’t replaced them with dental implants or dentures, it may feel possible to manage by eating without them. Some even find it gets easier with time. But the truth is, eating without teeth can create serious health concerns for your mouth and your overall body.
Here’s what you need to know:
Impact on Gums and Jaw Health
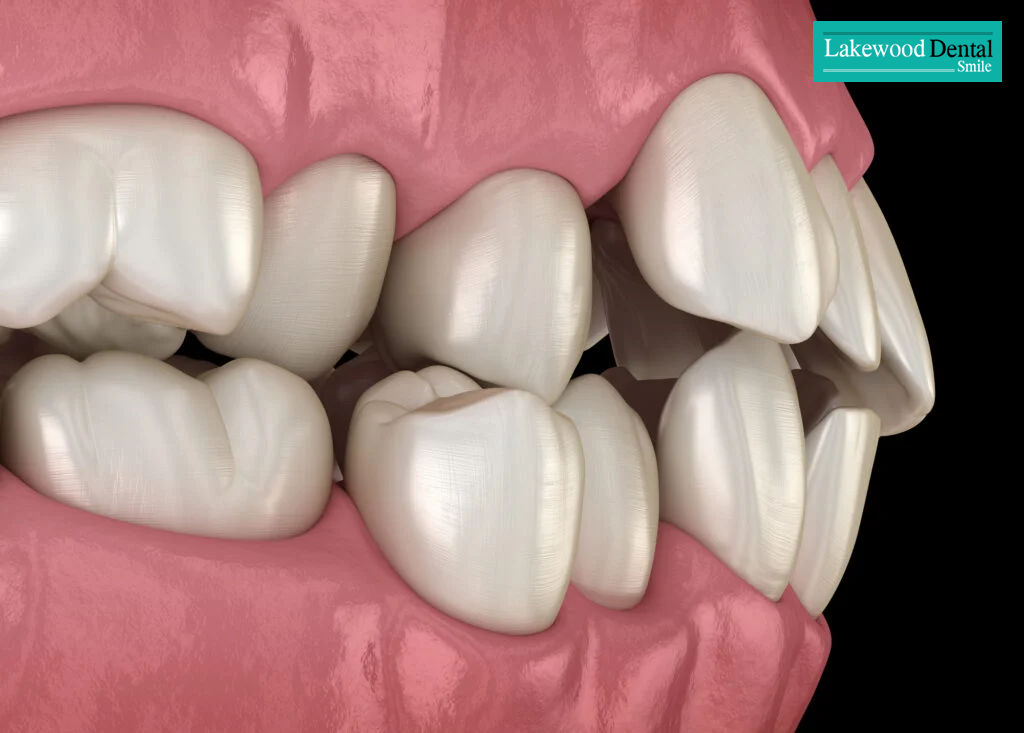
Chewing without teeth forces your gums and jaws to work much harder to break down food. This often leads to soreness, irritation, and even gum infections. Over time, it can also contribute to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems.
Your jawbone also needs stimulation from teeth or dentures to stay strong. Without it, the bone weakens, shrinks, and becomes more prone to fractures. While you can eat certain soft foods without teeth, this should only be a temporary solution.
Digestive and Nutritional Problems
Chewing is the first and one of the most important steps of digestion. Without it:
- Food isn’t broken down properly, making it harder for your body to absorb nutrients.
- Large food fragments can cause indigestion, bloating, and bacterial overgrowth in the gut.
- Chewing also signals your stomach and pancreas to release digestive acids and enzymes. Without that signal, digestion becomes less efficient.
A long-term “no-chew” diet not only limits the foods you can enjoy but also reduces the nutrition your body receives.
What Can You Do?
Living without teeth is not a healthy long-term plan. Teeth—or their replacements—play an essential role in both oral and overall health.
If cost, embarrassment, or other reasons are stopping you from replacing missing teeth, know that there are options. Dentures, dental implants, and other treatments can be tailored to your situation. At Lakewood Dental Smile, we can help create a plan that works best for your needs so you can eat, speak, and live comfortably again.